what was the first building in the world to have more than 100 floors

The 828 one thousand (ii,717 ft) tall Burj Khalifa in Dubai has been the tallest edifice since 2008.[1] The Burj Khalifa has been classified as Megatall.[2]
The tallest edifice in the world, every bit of 2022, is Burj Khalifa. The championship of "globe's tallest edifice" has been borne by various buildings, such as the 3rd-century Jetavanaramaya stupa, Lincoln Cathedral, the Empire State Building and the original Globe Trade Center.
Earlier the modern skyscraper era, betwixt c. 1311 and 1884, the tallest buildings and structures were mostly Christian churches and cathedrals. Before the 13th century, the tallest buildings in the world cannot be conclusively adamant. For case, the Lighthouse of Alexandria (completed virtually 280 BC) has been estimated to accept been 100 m (330 ft) alpine,[3] but its true summit is not known. For thousands of years, the Great Pyramid in Egypt was the tallest structure in the world until Lincoln Cathedral of 1311, but the Great Pyramid is not considered a building since it is not habitable. Similarly, the Eiffel Belfry was the world's tallest structure from 1889, when it was built, only not the tallest building.
The skyscraper was invented in Chicago in 1884 when the Home Insurance Building was constructed using a steel frame with curtain walls instead of load-bearing walls. For the next hundred years, the earth'south tallest building was always in the United States, with New York Urban center accumulating 86 years, and Chicago 30 years. After only over a century (1885–1998), the distinction moved to the Eastern Hemisphere. Malaysia was the offset country to intermission the Us' record of constructing the tallest buildings in the globe when the Petronas Twin Towers were completed in 1998. Taiwan'south Taipei 101 was the side by side to concur the record, beginning in 2004.
Definition of terms [edit]
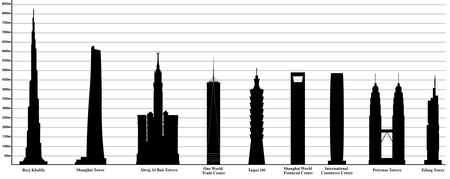
The tallest buildings in 2015
Meaning of "building" [edit]
The primeval structures now known to be the tallest in the globe were the Egyptian pyramids: the Bang-up Pyramid of Giza, at an original superlative of 146.5 thou (481 ft), was the tallest structure in the world for over 3,800 years, until the construction of Lincoln Cathedral in 1311. From then until the completion of the Washington Monument (capped in 1884) the world'due south tallest structures were churches or cathedrals. Later, the Eiffel Belfry and, still later, some radio masts and television towers, were the world'southward tallest structures.
However, though all of these are structures, some are not buildings in the sense of being regularly inhabited or occupied. It is in this sense of being regularly inhabited or occupied that the term "building" is generally applied when determining the earth's tallest building. The non-profit international system Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH), which maintains a set of criteria for determining the height of tall buildings, defines a "building" every bit "(A) structure that is designed for residential, business or manufacturing purposes" and that "has floors".[4]
Tall churches and cathedrals occupy a centre footing: their lower areas are regularly occupied, only much of their peak is in bell towers and spires which are non. Whether a church or cathedral is a "edifice" or merely a "structure" for the purposes of determining the title of "world's tallest building" is a subjective matter of definition (this commodity treats churches and cathedrals as buildings).
Determination of tiptop [edit]
The Council on Alpine Buildings and Urban Habitat uses three different criteria for determining the height of a tall building, each of which may requite a dissimilar result. "Height of the highest floor" is one criterion, and "acme to the height of any role of the building" is another, but the default benchmark used by the CTBUH is "peak of the architectural superlative of the building", which includes spires but not antennae, masts or flag poles.[4]
Earlier the 20th century [edit]
Before the 13th century [edit]

Early alpine buildings were like to the record-setting Egyptian pyramid structures. In 1400 BC the 70 k (230 ft) ziggurat of Dur-Kurigalzu was constructed in Republic of iraq, and in 601 BC the Etemenanki ziggurat of Babylon (91 grand (299 ft)) followed. The seventy g (230 ft) La Danta of El Mirador (Guatemala) and the 73 m (240 ft) Amaravati Stupa of Amaravathi (India) were constructed in around 300 BC.
The Lighthouse of Alexandria (Egypt) had a height of between 103 and 118 grand (338 and 387 ft) and existed between the 3rd century BC and 14th century CE.
The Pantheon in Rome, finished in the early on second century CE, has a ancient Roman height record from flooring to acme of 43.45 m (142.6 ft),[five] which exactly corresponds to the diameter of its interior space and was only slightly was surpassed by the Pont du Gard structure. The Hagia Sophia, built in 537 CE in Constantinople, reaches a pinnacle of 55 k (180 ft).
The ancient Kushan stupa of Kanishka (now in Pakistan, near Peshawar), completed around 200 CE, had a height of between 120 and 170 k (390 and 560 ft). The Chinese explorer Xuanzhang described it as the tallest building in the world in his book Records of the western Region. The Sri Lankan Jetavanaramaya stupa, constructed in the 3rd century, measured 122 k (400 ft) from its construction until the 11th century. Its electric current height is 71 m (233 ft).
Some other short-lived structure was the 6th-century wooden Yongning Pagoda (永宁宝塔) with a meridian of virtually 137 grand (449 ft)[vi] to 155 1000 (509 ft)[7] in Luoyang, Cathay.
Hwangnyongsa, or Hwangnyong Temple (also spelled Hwangryongsa), is a quondam Buddhist temple in the urban center of Gyeongju, Southward Korea. Completed in the 7th century, the enormous 9-storey structure was built entirely of interlocking timbers with no iron nails. It had a standing total height of 68 to 80 k (223 to 262 ft),[8] making it the tallest structure in East asia and the tallest wooden construction in the world at the time of its construction. Information technology was destroyed by invading Mongol forces in 1238. In 1057 the 100 thou (330 ft) wooden Shwesandaw Pagoda of Bagan, Myanmar, was constructed.
The Vimana of the Brihadisvara Temple, Thanjavur, completed in 1010 Ad is 66 m (217 ft) tall, slightly taller and older than Angkor Wat, Cambodia. The entire complex is built of granite. The 77 yard (253 ft) minaret of Koutoubia Mosque in Marrakesh, Morocco, includes a spire and orbs. It was completed under the reign of the Berber Almohad Caliph Yaqub al-Mansur around 1195.


The eastern spires of the Romanesque Speyer Cathedral, completed in 1106, reach a meridian of 71.3 chiliad (234 ft). The still-standing Torre Asinelli, completed some time before 1185, was originally seventy m (230 ft) tall, afterward raised to 92 m (302 ft). Malmesbury Abbey was built in 1180 and reached a pinnacle of 131 m (430 ft).
Churches and cathedrals: tallest buildings between the 13th and 20th century [edit]

Tallest buildings diagram from 1850
The world's tallest structures were churches or cathedrals from the 13th/14th century until 1884, and buildings until the outset of the 20th century. The Former St Paul's Cathedral (149 one thousand (489 ft)) in London and Lincoln Cathedral (160 one thousand (520 ft)) both surpassed not only any older tallest edifice, but also the tallest structures until then, the Pyramids. They were constructed from the twelfth century, reaching completion and their maximum summit in the 1310s (1314 and 1311 respectively). Lincoln Cathedral's spire collapsed in 1549, and its previous tiptop was not surpassed elsewhere for a long fourth dimension. St. Mary's Church in Stralsund became the world's tallest building after the plummet of the Lincoln spire. The 153 m (502 ft) central tower of St. Pierre's Cathedral in Beauvais was tallest from 1569 until it complanate in 1573, making St. Mary'south the tallest once again. In 1647, the bell tower of St. Mary's burned downwards, making the shorter Strasbourg Cathedral the world's tallest building.
It was not until the completion of the Ulm Minster in 1890 that the world'southward tallest building was again too the tallest building ever constructed, surpassing the original configuration of Lincoln Cathedral.
| Years tallest | Name | Location | Height | Increment | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13th century–1311[ commendation needed ] | Old St Paul's Cathedral | London | 149 m (489 ft) | 0% | Final completion in 1314. Destroyed in the Great Burn of London in 1666 |
| 1311–1549 | Lincoln Cathedral | Lincoln | 159.7 m (524 ft) | 7.two% | Tallest e'er building until 1890. Spire complanate 1549. |
| 1549–1569 | St. Mary'southward Church | Stralsund | 151 m (495 ft) | −5.4% | |
| 1569–1573 | St. Pierre'due south Cathedral | Beauvais | 153 chiliad (502 ft) | ane.iii% | Tower collapsed 1573 |
| 1573–1647 | St. Mary'southward Church | Stralsund | 151 thousand (495 ft) | −1.three% | Bell tower burned downward in 1647 |
| 1647–1874 | Cathedral of Our Lady of Strasbourg | Strasbourg | 142 one thousand (466 ft) | −6% | |
| 1874–1876 | Church of St. Nicholas | Hamburg | 147 g (482 ft) | iii.5% | |
| 1876–1880 | Rouen Cathedral | Rouen | 151 m (495 ft) | two.seven% | |
| 1880–1890 | Cologne Cathedral | Cologne | 157.38 thousand (516.3 ft) | 4.2% | Tallest structure Washington Monument from 1884 |
| 1890–present | Ulm Minster | Ulm | 161.53 m (530.0 ft) | 2.6% | Tallest structure Eiffel Tower from 1889 |
The 159.7 m (524 ft) height of Lincoln Cathedral is disputed past some,[9] but accepted past nigh sources.[10] [11] [13] [14] [15] The completion appointment for the spire is given as 1311 rather than 1300 by some sources.[16] Also the 149 1000 (489 ft) height of the spire of Old St Paul's Cathedral, destroyed by lightning in 1561, is disputed, for example past Christopher Wren (1632–1723), who suggested a acme of 140 m (460 ft).[17]
Fin de siècle [edit]
In 1890 Ulm Minster became the tallest church always congenital, only it was the final church to claim the position of tallest building, which eventually went to the Philadelphia City Hall in 1894, the first skyscraper taller than 150 m (490 ft) (or, depending on definition, the Mole Antonelliana in 1889).[18]
Among all structures, in 1884 the 169 grand (554 ft) Washington Monument had already overtaken the long-continuing record held by churches. Only 5 years later in 1889 information technology was significantly surpassed by the Eiffel Tower, which reached completely new heights at 300 yard (980 ft) (its 24 m (79 ft) antennas were added after 1957),[19] leaving heights of skyscrapers behind and opening up the supertall era, whose heights were only reached past the top of the Chrysler Building (319 m (i,047 ft)) in 1930 and fully overtaken by the Empire State Building in 1931.
Tallest structures since the 20th century [edit]

Since the completion of the Washington Monument in 1884, the world'south tallest structure has more often than not not likewise been the globe's tallest edifice. The exception is 1930–1954, when the Eiffel Tower was surpassed by the Chrysler Building in 1930, and in 1931 the Chrysler Building by the Empire State Building, only to be surpassed in plough by a succession of broadcast masts, starting with the Griffin Television Tower in Oklahoma, somewhen reaching the heights of megatall skyscrapers.
Even so, since the completion of the Burj Khalifa in 2010 the tallest building has once again been too the tallest structure past any criterion. It has the highest architectural chemical element, tip and occupied floor, and is the tallest structure of any kind always congenital, surpassing the (at present destroyed) 646.38 m (2,120.vii ft) Warsaw radio mast.
[edit]
Since the completion of the outset skyscraper taller than 150 m (490 ft), the Philadelphia City Hall in 1894 (or depending on definition the Singer Building in 1908) skyscrapers have consistently been the tallest buildings.
High-ascent blocks and early skyscrapers [edit]
Earlier skyscrapers, belfry blocks reached at various times and locations heights of 30 one thousand (98 ft) (equally in the city of Shibam) or fifty-fifty upwards to 100 m (330 ft) amongst the Towers of Bologna. Buildings that have been specifically chosen the get-go skyscrapers include:
- E. V. Haughwout Edifice, 24 yard (79 ft) tall, 5floors, first use of a passenger lift, built in 1857
- Equitable Life Edifice,[20] at least forty m (130 ft) tall, ix floors, congenital in 1870
- New York Tribune Building,[20] 79 m (259 ft) tall, 9 floors, congenital in 1875, expanded in 1907 to 19 floors
- Montauk Building,[21] 40 m (130 ft) tall, x floors, built in 1883
- Home Insurance Edifice,[22] 42 m (138 ft) tall, 12 floors, built in 1885
- Lancashire Insurance Building,[20] [23] ten floors, built in 1890
- Manhattan Building,[20] 68.3 m (224 ft) tall, 16 floors, built in 1891
- Monadnock Building,[21] 66 m (217 ft) alpine, 17 floors, congenital in 1891
Subsequently tape-setting early on skyscrapers include:
- New York Earth Building, 94 chiliad (308 ft), 1890
- Manhattan Life Insurance Building, 106 m (348 ft), 1894
[edit]

Comparison of the vanity height (as defined every bit the divergence betwixt the pinnacle top and the height to the floor of the highest occupied summit flooring) of some buildings which have been the world's tallest
After the structure of the first skyscraper taller than 150 m (490 ft), depending on definition the Philadelphia City Hall in 1894 or the Singer Building in 1908, the incrementation in the superlative category of supertall skyscrapers began with the construction of the Chrysler Building, followed by the Empire State Building, in New York City. The Chrysler Building was the beginning building in the world to break the 300 m (980 ft) barrier, and the Empire Country Building was the first edifice to have more 100 floors. Information technology stands at 381 m (1,250 ft) and has 102 floors. The adjacent tallest skyscraper was the Globe Merchandise Center, which was completed in 1971. The due north tower was 417 m (1,368 ft) and the south 415 grand (i,362 ft) alpine. It surpassed the height of the Empire State Building by 36 k (118 ft). 2 years subsequently the Sears Tower was built in Chicago, continuing at 442 thou (1,450 ft) with 110 floors, surpassing the height of the Globe Merchandise Eye past 25 1000 (82 ft). The Petronas Towers rose 10 meters above the Sears Tower, standing at a height of 452 m (ane,483 ft) and each having 88 floors.
In 2004, the structure of Taipei 101 brought the height of skyscrapers to a new level, standing at 508 thousand (ane,667 ft) with 101 floors. It is 59 k (194 ft) taller than the previous record-holders, the Petronas Towers. Burj Khalifa surpassed the peak of Taipei 101 by 319 m (1,047 ft) in 2009, making it threescore% taller.[24] Information technology has broken several skyscraper records, and it is almost twice equally tall as the Empire State Building. Burj Khalifa has besides broken the record of the world's tallest structure. However the majority of that height increment (29%) is gained from vanity meridian, the Burj Khalifa'southward highest occupiable floor is but 585 thou (1,919 ft) to a higher place basis. This would notwithstanding make it the tallest building in the earth just simply by 2 meters over the Shanghai Tower,[25] a substantially smaller margin than earlier.
- NOTE: The CTBUH defines a building as a supertall if information technology is 300 m (980 ft) or taller.[26]
[edit]
Since the early skyscraper boom that took place in North America, the meaning number of skyscrapers in North America have dominated the 100 tallest buildings in the globe. In 1930, 99 of the 100 tallest buildings in the earth were in North America. In the future, this per centum is expected to decline to but 22 percent.[24] The predominance of skyscrapers in North America is decreasing because of skyscraper construction in other parts of the world, especially in Asia. In Asia, there has been an increase in the number of supertall skyscrapers kickoff with the construction of Petronas Twin Towers. Currently, sixty of the earth'south 100 tallest buildings are in Asia (including the Eye East).
[edit]
Since the skyscraper era began, the great bulk of skyscrapers were used predominantly every bit office infinite. From 1930 to 2000, the percentage of office towers never fell below 86 percent, but in the future it is expected to be as depression as 46 percent.[24] By 2010, fewer than half of the 100 tallest buildings in the earth were function towers, the bulk being for residential and mixed use.[24] Only 4 of the ten tallest buildings in the world, and twenty-eight of the top fifty, were used primarily every bit offices.[27]
A mixed-utilise tall building is defined every bit having two or more than functions that occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space.[A] Support areas such as motorcar parks and mechanical found infinite practice not contribute towards mixed-apply status.[26]
Skyscrapers used primarily or exclusively as hotels or residential space are by and large shorter than part and mixed-apply buildings, with only a few supertall buildings of the residential or hotel types among the 100 tallest skyscrapers. The tallest completed residential buildings (minimum 85% residential) are Cardinal Park Tower, 111 Westward 57th Street, and 432 Park Avenue, all on Billionaire'southward Row in New York City.[28] The tallest completed hotels (primarily hotel space) are the Gevora Hotel, the JW Marriott Marquis Dubai twin towers, the Rose Tower, and the Burj Al Arab, all in Dubai.[29]
[edit]
The post-obit list of tallest buildings is based on the default metric of CTBUH,[22] that of measuring to the highest architectural element. Other criteria would generate a unlike list. Shanghai World Financial Center is non on the above list, but information technology surpassed Taipei 101 in 2008 to become the building with the highest occupied floor. Using the criterion of highest tip (including antennae), the World Trade Heart in New York Urban center was the world'due south tallest building from 1972 to 2000, until the Sears Tower in Chicago (which already had a higher occupied flooring than the Earth Merchandise Heart) had its antenna extended to requite that building the world's tallest tipl a championship it held until the 2010 completion of Burj Khalifa. Petronas Towers and Taipei 101 were never the world's tallest buildings by the highest–tip criterion.
| Years tallest | Name | Location | Summit | Increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1894–1908 | Philadelphia City Hall | Philadelphia | 167 m (548 ft)[30] | 0% |
| 1908–1909 | Vocalist Building | New York Metropolis | 192 yard (630 ft) | 15% |
| 1909–1913 | Metropolitan Life Tower | 213 m (699 ft) | eleven% | |
| 1913–1930 | Woolworth Building | 241 1000 (791 ft) | thirteen% | |
| 1930 | forty Wall Street | 283 m (928 ft) | 17% | |
| 1930–1931 | Chrysler Building | 318.nine chiliad (1,046 ft) | thirteen% | |
| 1931–1971 | Empire State Building | 381 m (1,250 ft) | nineteen% | |
| 1971–1973 | World Merchandise Center | 417 m (i,368 ft) | 9% | |
| 1973–1998 | Sears Tower | Chicago | 442 m (1,450 ft) | 6% |
| 1998–2004 | Petronas Towers | Kuala Lumpur | 452 yard (1,483 ft) | 2% |
| 2004–2010 | Taipei 101 | Taipei | 510 m (1,670 ft) | 13% |
| 2010–present | Burj Khalifa | Dubai | 828 m (2,717 ft) | 62% |
See also [edit]
- History of tallest skyscrapers
- List of tallest buildings and structures
- Listing of Egyptian pyramids
- Listing of tallest buildings
- Listing of tallest churches
- List of tallest structures built before the 20th century
- Listing of oldest known surviving buildings
Notes [edit]
- A. ^ This significant proportion tin can be judged as 15% or greater of either the total floor surface area, or the total building meridian in terms of number of floors occupied for the function. However, intendance should be taken in the case of supertall buildings. For example, a 20-story hotel function as part of a 150-story tower does not comply with the xv% dominion, though this would conspicuously constitute mixed use.
References [edit]
- ^ "Burj Dubai now a tape 688m tall and continues to rise". Emaar Properties. 1 September 2008. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ^ "The Tallest twenty in 2020: Entering the Era of the Megatall". CTBUH. 8 December 2011. Retrieved 19 October 2012.
- ^ Clayton, Peter A. (2013). "Affiliate 7: The Pharos at Alexandria". In Peter A. Clayton; Martin J. Price (eds.). The Vii Wonders of the Aboriginal Earth. London: Routledge. p. 147. ISBN9781135629281.
- ^ a b Gerometta, Marshall. "Summit: The History of Measuring Tall Buildings". Council on Alpine Buildings and Urban Habitat. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ *Rasch, Jürgen (1985), "Die Kuppel in der römischen Architektur. Entwicklung, Formgebung, Konstruktion", Architectura, xv: 117–139 (119)
- ^ "北魏洛阳永宁寺塔基遗址新出土的彩绘泥塑造像". 手机360doc (in Chinese). 10 August 2021. Retrieved 25 February 2022.
- ^ "关于北魏洛阳永宁寺塔复原的再研究". 道客巴巴 (in Chinese). 24 Oct 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2022.
- ^ Lee, Soyoung; Leidy, Denise Patry (2013). Silla : Korea'southward gilt kingdom. Lee, Soyoung, 1971, Leidy, Denise Patry,, Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York, N.Y.),, Samsŏng Chŏnja,, National Endowment for the Arts, Han'guk Kukche Kyoryu Chaedan. New York. p. 22. ISBN9781588395023. OCLC 862096677.
- ^ Kendrick, A. F. "The Project Gutenberg eBook of The Cathedral Church of Lincoln". George Bell & Son. Archived from the original on 4 Feb 2012. Retrieved 28 November 2009 – via Gwydir.demon.co.uk.
- ^ Haughton, Brian (2007). Hidden History: Lost Civilizations, Secret Knowledge, and Ancient Mysteries . p. 167.
- ^ Wood, Michael; Woods, Mary B. (2009). Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. p. 41.
- ^ Porter, Darwin; Prince, Danforth (2010). Frommer'southward England 2010. p. 588.
- ^ Taber, Mary Jane (1905). The Cathedrals of England: an business relationship of some of their distinguishing characteristics. p. 100.
- ^ "A Brief History of the World's Tallest Buildings". Fourth dimension magazine.
- ^ "Cathedrals and the nativity of liberty". Institute of Public Affairs Australia. Archived from the original on three March 2016. Retrieved half-dozen May 2011.
- ^ Benham, William (1902). One-time St. Paul's Cathedral. London: Seeley & Co at Projection Gutenberg
- ^ "Mole Antonelliana". Museo Nazionale del Cinema (Italian National Film Museum) website. Maria Adriana Prolo Foundation. Retrieved xviii March 2014.
Structure was completed in 1889... At the time of its completion, at 167.5 meters in height, it was the tallest masonry building in all of Europe.
- ^ Lieber, John (5 January 2022). "Which is taller, the Chrysler Building or the Eiffel Tower?". BindleyHardware & Co . Retrieved 19 February 2022.
- ^ a b c d "The Birth of Height: What was the Globe's First Skyscraper?". Building the Skyline. 7 October 2017. Retrieved 17 July 2020.
- ^ a b Kamin, Blair. "Column: The same people who demoted Willis Belfry could strip Chicago of another skyscraper title". Chicago Tribune . Retrieved nineteen November 2020.
- ^ a b Wood, Anthony, ed. (2015). 100 of the world's tallest buildings. Victoria, Australia: The Images Publishing Group. ISBN978-1-86470-651-2. OCLC 930796742.
- ^ Greyness, Christopher (15 May 1988). "IN THE NEW YORK REGION; The Lost Skyscrapers of Bygone New York". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 17 July 2020.
- ^ a b c d "The History of Measuring Alpine Buildings". Quango on Alpine Buildings and Urban Habitat. 2008. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011. Retrieved sixteen February 2010.
- ^ "Shanghai Belfry - The Skyscraper Center". skyscrapercenter.com . Retrieved 23 Baronial 2020.
- ^ a b "Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat". ctbuh.org . Retrieved 23 August 2020.
- ^ "Tallest unmarried-function function buildings in the world (every bit of December 2009)" (PDF). ctbuh.org. Quango on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat. December 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 February 2010.
- ^ "Search results - tallest completed residential buildings (as of 2018)". skyscrapercenter.com. Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ^ "Search results - tallest completed hotels (equally of 2018)". skyscrapercenter.com. Council on Alpine Buildings and Urban Habitat. Retrieved xix November 2018.
- ^ "Philadelphia City Hall - The Skyscraper Center". skyscrapercenter.com . Retrieved 17 February 2022.
External links [edit]
- These are the globe'south tallest structures throughout history, v Sep 2019, Visual Capitalist, World Economic Forum
- 100 Tallest Completed Buildings in the World, Skyscraper Center
- Buildings database, Structurae.net
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_world%27s_tallest_buildings#:~:text=The%20height%20of%20skyscrapers,-Comparison%20of%20the&text=The%20Chrysler%20Building%20was%20the,have%20more%20than%20100%20floors.
0 Response to "what was the first building in the world to have more than 100 floors"
Post a Comment